Overqualified Housewives: AI Semantic Candidate Discovery
AI-powered recruitment search combining LLM extraction, pgvector semantic matching, and multi-factor weighted scoring for finding returning women professionals through natural language queries.
Executive Summary
CyberMind Works built an AI-powered semantic candidate discovery system for Overqualified Housewives, a platform connecting returning women professionals with employers. The system enables employers to search for candidates using natural language queries like "Frontend developer with 2 years of React experience" while maintaining traditional filter-based search capabilities.
Built using LLM-powered structured extraction, PostgreSQL pgvector for semantic search, and a multi-factor weighted scoring engine, the system addresses the unique challenge of matching non-linear career profiles and diverse skill narratives. The platform combines Gemini/OpenAI APIs for query understanding with vector similarity search and traditional filters to deliver highly relevant candidate matches.
This case study explores the technical architecture, semantic search challenges, and engineering decisions that enable the platform to deliver accurate candidate discovery while maintaining cost efficiency through prompt caching and optimized AI usage.
Problem Statement
Vocabulary Mismatch
- Traditional keyword search can't match synonyms like "UI Engineer" with "Frontend Developer"
- Fails to recognize similar technologies like "React" and "React.js"
- Great candidates are missed entirely due to exact keyword requirements
Over-Filtering Friction
- Too many dropdowns and filters reduce platform usage
- Employers abandon complex filter combinations
- Lower conversion rates due to search complexity
Low Semantic Relevance
- Qualified candidates get buried in results despite having matching skills
- Exact keyword presence overrides actual relevance
- No understanding of skill relationships and context
Non-Linear Career Profiles
- Women returning from career breaks have diverse skill narratives
- Traditional search fails for non-linear timelines
- Career gap context not considered in matching
Natural Language Query Support
- Employers want to search using plain English descriptions
- No support for queries like "React developer with 2 years experience in Bangalore"
- Forces users into rigid filter-based workflows
Solution Overview
CyberMind Works created a production-grade AI-powered semantic search pipeline that converts natural language queries into ranked, relevant candidate matches. The system combines:
- LLM-Powered Extraction — Converts natural language into structured requirements (skills, location, experience, degrees, preferences) using Gemini/OpenAI APIs
- Semantic Vector Search — PostgreSQL pgvector similarity search over multiple profile embeddings (skills, education, experience, industry)
- Structured Filters — Traditional constraints like city, work category, salary expectations, and employment status
- Multi-Factor Weighted Scoring — 20+ signals normalized dynamically so sparse profiles don't get unfairly penalized
- Prompt Caching & Analytics — Stores query interpretation for cost control and captures search behavior for continuous improvement
This approach delivers highly relevant matches for non-linear career profiles while maintaining cost efficiency through prompt caching and explainable results through transparent scoring.
Technical Architecture
A pragmatic architecture combining LLM extraction, pgvector semantic search, and dynamic scoring with intelligent caching for cost control.
System Architecture
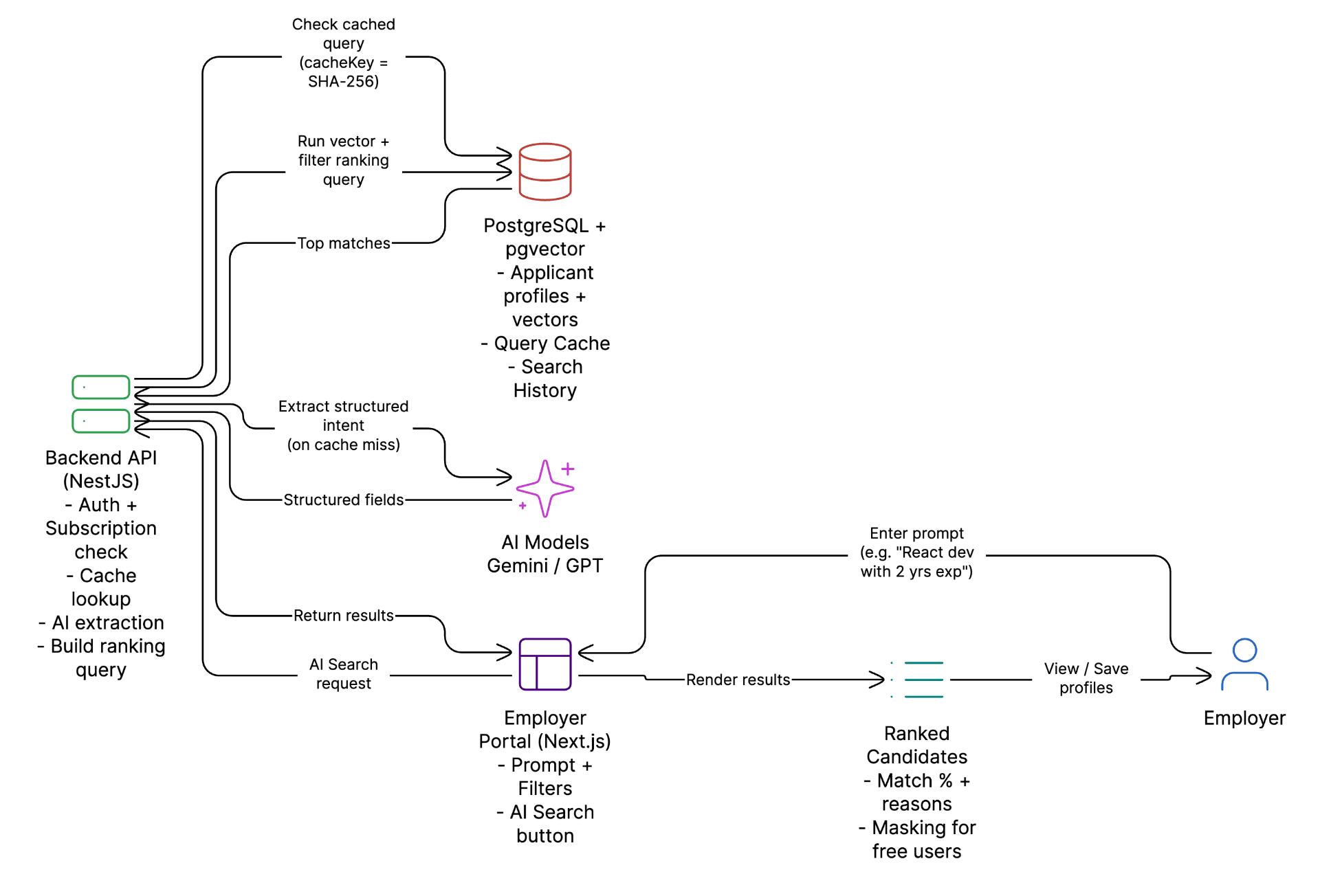
Frontend (Next.js)
- Natural language search input
- Standard filters (location, work model, role)
- AI model selection (beta users)
- Cache mode toggle (global vs user-specific)
Backend (NestJS)
- Auth + subscription enforcement
- Prompt normalization + SHA-256 hashing
- Cache lookup in prompt_query_cache
- LLM extraction (Gemini / OpenAI)
- Dynamic SQL generation
- Search history instrumentation
PostgreSQL + pgvector
- Applicant tables + vector columns
- Query cache + search history
- Hybrid scoring query execution
- Multi-vector profile storage
LLM Extraction Pipeline
Prompt → Normalize → Hash (SHA-256) → Cache lookup → Extract structured fields → Skills, experience, location, degrees, work preferences
Intelligent Caching
Caches interpreted query (not just results) for cost reduction, faster UX, and consistent results. Supports global and employer-scoped cache modes.
Multi-Vector Strategy
Personal info, experience, education, location, career break, skills, functional area, industry, and language vectors computed separately with cosine similarity.
Multi-Factor Weighted Scoring
The ranking system computes an overall weighted score from 20+ signals, with dynamic normalization to handle incomplete profiles fairly.
Scoring Factors
Dynamic Weight Normalization
Weights are normalized based on available data in candidate profiles and query intent:
- Missing fields don't destroy candidate scores
- Explicit employer requirements get priority
- Total weight remains stable (sums to 1.0)
Skill Matching with Confidence Scoring
Skills are not treated as plain keywords. Each skill has a confidence score derived from multiple evidence sources:
Experience evidence
Strongest
Project mentions
Strong
Certifications
Moderate
Achievements
Moderate
Explicit proficiency
Direct
User Experience Design
The UI is designed as progressive disclosure—start with one natural-language box (lowest friction), with filters available for precision, and explainable results to build trust.
Natural Language First
Single search box accepts plain English queries. No complex filter configuration required to start.
Match Quality Tiers
Results labeled into human-readable tiers for quick assessment:
Match Reasons for Trust
Each result includes top reasons to reduce employer skepticism:
Security, Privacy & Monetization
The system balances user privacy, data security, and commercial objectives through careful access controls and subscription gating.
Subscription Gating
AI Search positioned as conversion lever—non-subscribers preview masked results, subscribers get full visibility.
Data Masking
PII fields (last name, address) masked for non-subscribed users while still allowing relevance assessment.
Query Safety
Dynamic SQL assembly uses parameterized inputs and sanitization to reduce injection risk.
Beta Gating
Premium model access enforced at API boundary—prevents unauthorized access to expensive AI models.
Technology Stack
Frontend
Backend
Database
AI/LLM
Caching
Search
Multi-Model Support
Multiple AI models supported for cost/performance tradeoffs, resilience, and controlled experimentation:
Gemini 2.5 Flash
Default - fast & cost-effective
Gemini 2.5 Pro
Higher accuracy
OpenAI GPT-4o
Beta/testing
OpenAI GPT-5 family
Premium tier
Technical Challenges & Solutions
Weight balancing across many factors
Normalization + explicit requirement boosts and iterative tuning
Handling incomplete profiles
Multi-vector approach + safe similarity defaults avoid penalizing sparse resumes
Model variability and outages
Multi-model routing + downtime handling provides reliability
Keeping performance acceptable
Cache-first flow + vector indexes + pagination + thresholds keep runtime stable
Business Impact
Product Impact
- Faster candidate discovery via natural language
- Higher perceived 'intelligence' of the platform
- Better search satisfaction due to semantic relevance
- Explainable results build employer trust
Commercial Impact
- Subscription conversion uplift (AI Search as premium differentiator)
- Reduced AI inference costs via caching (especially with Flash as default)
- Controlled rollout of expensive models through beta gating
- Search analytics for platform optimization
20+
Scoring Signals
9+
Vector Types
4
AI Models Supported
SHA-256
Query Caching
Conclusion
This engagement showcases CyberMind Works' ability to deliver production-ready AI search systems built for real-world recruitment challenges. The Overqualified Housewives AI Search feature demonstrates how LLM extraction, semantic vector search, and multi-factor scoring can create a premium candidate discovery experience for non-linear career profiles.
By combining natural language query understanding with PostgreSQL pgvector semantic matching, traditional filters, and weighted scoring algorithms, the platform enables employers to find returning women professionals through intuitive search while maintaining cost efficiency through prompt caching and explainable results through transparent scoring.
Designed for continuous improvement, the system captures search behavior analytics, supports evolving candidate profiles, and maintains high relevance without unnecessary infrastructure complexity. This makes AI Search not only a better way to find candidates but also a high-leverage product capability that directly supports subscription growth and platform engagement.
About Us
Portfolio
Careers
CyberMind Works LLP
10/15, K.M Towers - 1st Floor, Chakrapani Road,
Guindy, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, 600042
Copyright © 2026, CyberMind Works | All rights reserved.
